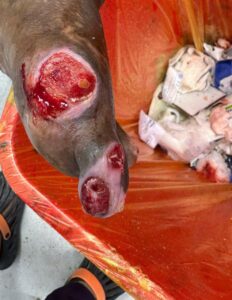
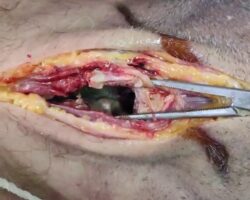
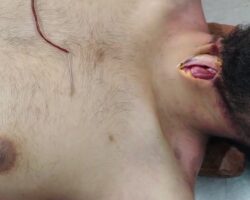
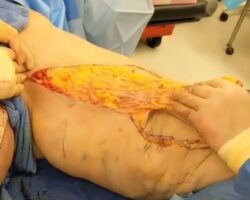
Videos show the process of cleaning a foot wound in a patient with advanced diabetes. The doctor removes all necrotic tissue using scissors and a scalpel, which is very important to prevent infection and sepsis.
Severe diabetics often have poorly controlled blood sugar levels, which frequently leads to nerve damage and poor blood circulation in various parts of the body, most commonly the feet. This phenomenon is even called diabetic foot.
The combination of nerve damage, weakened immunity, and poor circulation means that even minor injuries can develop into serious infections or necrosis. Without treatment, there is a risk of gangrene or amputation. Prompt wound care is therefore essential for diabetics.
Prevention is key: regular foot checks, proper hygiene, suitable footwear, and strict blood sugar control significantly reduce the risk of necrosis. Diabetics should seek medical attention immediately for any foot injury, redness, blisters, or dying tissue. Timely intervention can make the difference between full recovery and severe, permanent foot damage.